What We Know about ADHD and Marijuana?
Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a multifaceted brain disorder marked by inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity. These symptoms typically manifest in childhood by age 12 but can persist into adulthood. marijuana, as a potential treatment for ADHD, may offer relief from these symptoms in some cases.
Key Symptoms of ADHD
ADHD often shows up in ways you might not expect. You might find yourself drifting off during important tasks (inattention), feeling like you have endless energy. Still, you can't channel it (hyperactivity), struggle to stay on one topic for long (lack of focus), or act on a whim without thinking things through (impulsivity). It's a unique mix that can be challenging but manageable with the proper support.
Inattention:
- ADHD patients have difficulty maintaining attention. They frequently make careless mistakes and forget daily tasks such as appointments, commitments, or responsibilities. Patients may struggle to stay focused on tasks or conversations.
- Having ADHD makes organizing tasks and effective time management more difficult. There is a lack of attention to detail and occasional avoidance of tasks requiring sustained mental effort. Procrastination is a common trait.
- People with ADHD can get sidetracked by their random thoughts or surroundings, often resulting in mistakes at work or other tasks.
Hyperactivity:
Patients may fidget excessively or have trouble squirming in their seats with frequent tapping of their hands or feet.
- This restlessness results in a feeling of constantly being on the go or unable to relax. They may have problems finding it hard to stay seated in formal situations.
- Excessive talking may challenge communication, often interrupting conversations.
Impulsivity:
Hasty actions that occur without forethought or engage in risky behaviors. They often speak out of turn without 'reading the room.'
- Patients make hasty, impulsive decisions without considering long-term consequences.
- They often have difficulty waiting in lines or for their turn.
Emotional and Behavioral Symptoms in ADHD
- Mood Swings: Experiencing rapid and intense changes in mood.
- Low Frustration Tolerance: Becoming easily frustrated or irritated.
- Stress Management Issues: Difficulty coping with stress or managing emotional responses.
- Poor Self-Esteem: Feeling inadequate or having a negative self-image.
- Difficulty Completing Tasks: Patients start many projects but rarely finish them.
Relationships and Social Issues
- Problems with Relationships: Having frequent conflicts or misunderstandings with friends, family, or colleagues.
- Impatience: Finding it challenging to wait for others or listen without interrupting.
- Impulsivity in Social Settings: Saying or doing things without considering the impact on others.
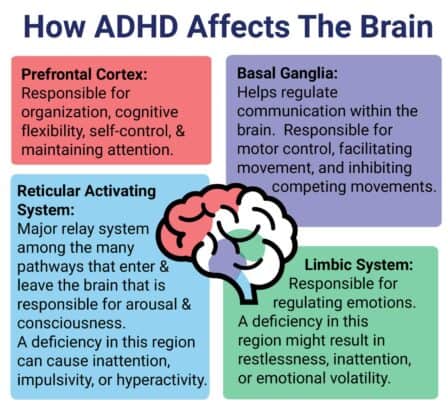
Brain Structures and Functions Linked to ADHD
While the exact causes of ADHD are unknown, studies have identified several key neurological mechanisms that play a role in the disorder:
- Neurotransmitter Imbalance: A well-documented difference in the ADHD brain is an imbalance of certain neurotransmitters, particularly dopamine and norepinephrine. These chemicals play crucial roles in attention, motivation, and reward processing. Individuals with ADHD often have lower levels of dopamine, which can affect their ability to maintain focus and control impulses.
- Structural Brain Differences: Imaging studies show fascinating structural differences in key areas like the prefrontal cortex, basal ganglia, and cerebellum. The prefrontal cortex, responsible for crucial executive functions such as decision-making and impulse control, often behaves differently or develops uniquely. Then, the basal ganglia, involved in motor control and cognitive functions—shows abnormalities linked to hyperactivity and impulsivity. The cerebellum also plays a role in these differences. It's incredible how these brain regions can shape one's behavior differently.
- Functional Brain Differences: The attention network—the prefrontal cortex, anterior cingulate cortex, and parietal cortex—acts differently in those with ADHD. This unique wiring often leads to struggles in maintaining focus and ignoring distractions. Have you ever been in the middle of a task only to be sidetracked by the slightest noise or a fleeting thought? It's like trying to concentrate in a room of people shouting different things simultaneously! It's frustrating, yet it's a part of how their minds work.
Common ADHD Treatments (medications, therapy, lifestyle changes)

Management and Treatment:
- Medications: Stimulants (e.g., methylphenidate, amphetamine) and non-stimulants (e.g., atomoxetine).
- Behavioral Therapies: Cognitive-behavioral therapy (CBT), behavior modification, and psychoeducation.
- Lifestyle Adjustments: Structured routines, organizational aids, and support groups.
What are Cannabis and THC and CBD Primary Components?
Medical marijuana uses cannabis to treat various health conditions. There are over 100 compounds, or cannabinoids, in the plant. CBD (cannabidiol) and THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) are the most important.
Like other synthetic drugs, marijuana can help with specific conditions, but it's not a cure-all. CBD, one of the most studied compounds, is abundant in hemp plants and is known for its anti-inflammatory properties. CBD might help with ADHD symptoms. THC, another compound, is psychoactive and can cause hallucinogenic effects, making it popular for casual, non-medical use.
Marijuana plants contain up to 40% CBD. While CBD is generally safe, THC can act as a depressant or stimulant, leading to side effects. Doctors consider the anti-inflammatory benefits of CBD against the potential psychological risks of THC.
How Marijuana Treatment for ADHD Might Alleviate Symptoms
- Dopamine Regulation: Marijuana, mainly THC, influences dopamine levels in the brain. The dopamine neurotransmitter is involved in attention and reward pathways. Dopamine disruption often dysregulates these pathways in individuals with ADHD.
- Anxiety Reduction: CBD, a non-psychoactive component of cannabis, may help reduce anxiety, which can be a comorbid condition with ADHD. Lower anxiety levels improve focus and reduce hyperactivity.
- Neurotransmitter Modulation: Your brain controls the release of chemical neurotransmitters, including those involved in attention and impulse control. By interacting with cannabinoid receptors, marijuana might help balance these chemicals.
Using Cannabis as ADHD Treatment
Using marijuana to treat ADHD is hotly debated. While THC and CBD might help with ADHD symptoms, the research shows mixed results. Although some people report benefits, more studies are needed.
Research Overview on Cannabis and ADHD
Here's an overview of existing research studies on marijuana and ADHD:
1. Thomas Jefferson University Study (2024): Researchers at Thomas Jefferson University conducted a scoping review focusing on how marijuana interacts with the endocannabinoid system to influence ADHD symptoms. They found that marijuana, particularly cannabidiol (CBD), might affect attention, hyperactivity, and anxiety1. However, the complexity of ADHD presentations and the variety of marijuana products pose significant research challenges.
2. Susan A. Stoner, PhD (2017): This study highlighted that while there is widespread belief in the medicinal benefits of marijuana for ADHD, there is virtually no rigorous, experimentally controlled research evidence to support this. The study showed that individuals with ADHD are at higher risk for developing marijuana use disorders2.
3. Neuroscience News Review (2024): A review by Neuroscience News summarizes the findings from different studies, showing that cannabis interacts with the endocannabinoid system, potentially influencing ADHD symptoms. However, legal restrictions limit the research and the variability in marijuana products and ADHD presentations3.
While these studies suggest that while marijuana may help with ADHD symptoms, the evidence is still limited. More research is needed to draw definitive conclusions.
Current State of Research for ADHD and Marijuana Treatment
Scientists disagree on whether marijuana is effective for ADHD. Some studies show possible benefits, but others emphasize the risks. For example, a small 2020 study found that higher doses of medical cannabis components, like CBD, reduced the need for other ADHD medications. However, a 2023 review concluded that there isn't enough proof to recommend marijuana for managing ADHD symptoms.
Structural Brain Differences: Research has noted that people with ADHD who use marijuana may have structural brain differences compared to those who do not.
Findings on the Potential Benefits of Cannabis for ADHD Symptoms
Here are some findings on the potential benefits of cannabis for ADHD symptoms:4
1. Improved Focus: Some studies suggest that marijuana, particularly strains high in CBD, may help improve focus and attention in individuals with ADHD.
2. Reduced Hyperactivity: There is evidence that cannabis can help reduce hyperactivity and impulsivity, which are common symptoms of ADHD.
3. Anxiety Relief: Cannabis, especially CBD, has been found to have anxiolytic properties, which can help alleviate anxiety often associated with ADHD.
4. Alternative to Traditional Medications: For some individuals, cannabis may serve as an alternative to traditional ADHD medications, which can have significant side effects.
Anecdotal Evidence rom Individuals with ADHD who Use Cannabis
Here are some anecdotal evidence and patient reports on cannabis treatment for ADHD:
1. Case Reports (2022): A report described three males (ages 18, 22, and 23) who integrated cannabis into their treatment regimen. They reported subjective improvements in symptoms and quality of life1. Improvements were noted on validated rating scales, such as the PHQ-9 (depression) and SCARED (anxiety), with reductions ranging from 8 to 22 points (30-81%) and 0 to 27 points (up to 33%), respectively. Mild adverse events included short-term memory problems, dry mouth, and sleepiness.5
2. Australian Case Study: A 50-year-old male with severe depression, anxiety, and ADHD reported that cannabis helped calm his brain, allowing him to focus, relax, and sleep. However, he also experienced challenges with dependence and potential interactions with his ADHD medications.6
3. Patient Reports: Many people with ADHD say that using cannabis, primarily THC, helps them manage symptoms like emotional regulation, impulse control, and focus. Some find it a good alternative to traditional ADHD medications, which can have significant side effects.7
Some individuals report that cannabis helps with ADHD symptoms like restlessness, impulsivity, and difficulty focusing. Some users find that cannabis helps limit distractions, reduces anxiety, and alleviates side effects from ADHD medications. The non-psychoactive component, CBD (cannabidiol), may help regulate brain activity and improve symptoms.
- Restlessness and Hyperactivity: Some users find that cannabis helps them feel more relaxed and less restless, which can be beneficial for managing hyperactivity.
- Impulsivity: Marijuana might help reduce impulsive behaviors and promote a sense of calm with less anxiety.
- Focus and Attention: While this is more controversial, some individuals report that marijuana as ADHD treatment helps them focus better and limit distractions, though this effect can vary widely.
Potential Risks and Side Effects of Using Cannabis for ADHD
Despite potential benefits, marijuana treatment may carry possible adverse effects such as substance use disorder or cognitive impairment. Using marijuana, especially with high THC content, can lead to substance use disorder and may interact with ADHD medications. This disorder (SUD) is notably higher in individuals with ADHD who use cannabis.
Cannabis Interactions with ADHD Medications
Cannabis can interact with several medications, particularly the stimulant medications used for ADHD. Here are some common ADHD medications that may be affected by cannabis use:
1. Methylphenidate (Ritalin, Concerta): Combining marijuana with methylphenidate can lead to cardiovascular complications and may reduce the therapeutic effects of the medication.
2. Amphetamine (Adderall, Vyvanse): Similar to methylphenidate, combining marijuana with amphetamine can increase the risk of cardiovascular issues and may alter the medication's effects.8
3. Non-stimulant medications (Strattera, Intuniv): While there is less research on interactions with non-stimulant medicines, it's still important to be cautious, as cannabis can affect how these medications work.
Legal Status of Cannabis (Medical vs. Recreational Use)
Many states have legalized cannabis for both medical and casual use, but it remains illegal at the federal level. Federal cannabis restrictions limit the amount of reliable research data available on its potential effects. A lack of data may further complicate access to marijuana for ADHD treatment purposes. There isn't enough conclusive research to recommend marijuana as a primary treatment for ADHD.

Legal and Social Implications of Cannabis Use in ADHD
Legal and social implications of marijuana use for ADHD are many and can vary depending on the region. Here are some key points to consider:
Legal Implications
· Medical vs. Recreational Use: Cannabis laws differ significantly between regions. In some places, medical marijuana is legal. It can be prescribed for ADHD, while in others, it is only available for recreational use.
· Employment: Even if you're using cannabis for medical reasons, it could still affect your job prospects. Some employers have strict rules against marijuana use, which might put your job at risk.
· Legal Standing: In some countries, cannabis is still illegal. So, having or using it could land you in legal trouble.
Social Implications
· Stigma: Despite growing acceptance, there is still a stigma associated with marijuana use, which can affect social relationships and how others perceive users.
· Public Perception: The perception of marijuana for ADHD treatment is conflicted. While some believe in its benefits, others are skeptical and concerned about potential risks4.
· Impact on Relationships: Marijuana use can affect personal and professional relationships, especially if it leads to dependence or conflicts with other medications.
In Summary
ADHD doesn't look the same for everyone. Each person experiences it differently, with their symptoms and challenges. It's essential to have a healthcare provider who can help you navigate your own personal ADHD journey. Of course, to start using cannabis for ADHD, you will need get a medical marijuana card.

